Projections and Manifolds in XAI
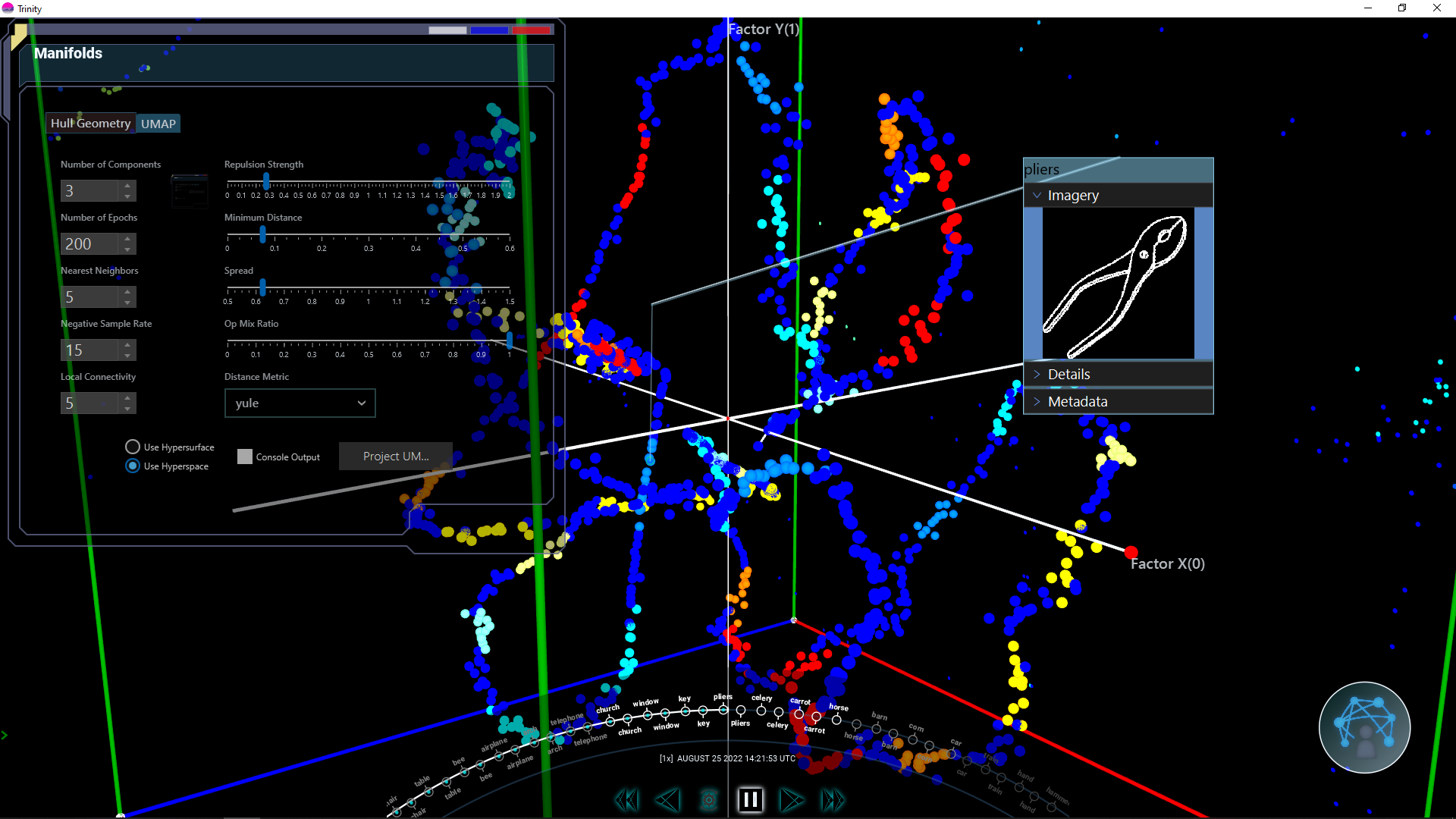
Understanding high-dimensional data through projections and manifold learning is crucial for explainable AI. These techniques help visualize complex relationships and make model behavior more interpretable by reducing dimensionality while preserving important structural information.
Key Techniques
Linear Projections
Explore traditional dimensionality reduction methods like PCA and LDA that project data onto lower-dimensional spaces while maximizing variance or class separation.
Nonlinear Manifolds
Discover complex data structures using advanced techniques like t-SNE and UMAP that can capture nonlinear relationships and local structure in the data.
Topological Analysis
Analyze the shape and structure of data manifolds using persistent homology and other topological data analysis methods to understand global patterns.
Implementation Example
Here's a simple example of manifold learning implementation:
import numpy as np
from sklearn.manifold import TSNE
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
def analyze_manifold(X, n_components=2):
# Initial dimensionality reduction with PCA
pca = PCA(n_components=min(50, X.shape[1]))
X_pca = pca.fit_transform(X)
# Nonlinear manifold learning with t-SNE
tsne = TSNE(n_components=n_components)
X_manifold = tsne.fit_transform(X_pca)
return X_manifold, pca.explained_variance_ratio_
Best Practices
- Start with linear projections before exploring nonlinear methods
- Validate projections using multiple techniques
- Consider the trade-off between global and local structure preservation
- Use appropriate perplexity and learning rate parameters
- Evaluate the quality of embeddings using quantitative metrics